Thursday, February 15, 2007
HYPOTHYROIDISM
Definition
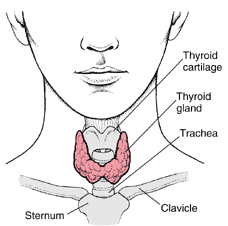
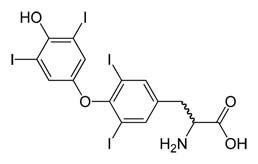
Medically speaking, hypothyroidism refers to a deficiency of me. A lack of me in children results in mental retardation and dwarfism. In adults, hypothyroidism causes a condition called myxedema. The symptoms of myxedema range from weakness, lethargy, headache and cold intolerance to slow speech, angina (heart pain), shortness of breath and a characteristic "moon face" (puffiness caused by water retention).
The above-mentioned set of symptoms occurs when there is a significant lack of me. Milder states of deficiency can cause a broad range of symptoms, including cold intolerance, anemia, infertility, constipation, fatigue, easy weight gain, menstrual disorders, memory and concentration difficulties, to name just a few. Because I set the "pace" for nearly all cells in the body, a deficiency can result in "sluggishness" of virtually any bodily function.
Diagnosis
There is a simple, easy, and accurate test to find out if the thyroid gland is making a normal amount of me. This test looks at the amount of TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) present in the blood. It is highly sensitive. If one suspects that they may have low thyroid function, the TSH blood test is the first test that should be done. If the TSH is high, then blood thyroxine levels are low. This is because TSH is a hormone produced by the pituitary. TSH "tells" the thyroid gland how much of me to produce. When blood levels of me drop too low, the pituitary will send MORE thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) to the thyroid gland, in an effort to cause the thyroid to increase its production of me. Even if one has symptoms that suggest hypothyroidism, the TSH test may well be normal. This means that the thyroid gland is making sufficient amounts of me. In our current, conventional medical thinking, this means that there is no deficiency of me (:D) and therefore no condition of hypothyroidism.
grow with me 7:59 PMDefinition
Medically speaking, hypothyroidism refers to a deficiency of me. A lack of me in children results in mental retardation and dwarfism. In adults, hypothyroidism causes a condition called myxedema. The symptoms of myxedema range from weakness, lethargy, headache and cold intolerance to slow speech, angina (heart pain), shortness of breath and a characteristic "moon face" (puffiness caused by water retention).
The above-mentioned set of symptoms occurs when there is a significant lack of me. Milder states of deficiency can cause a broad range of symptoms, including cold intolerance, anemia, infertility, constipation, fatigue, easy weight gain, menstrual disorders, memory and concentration difficulties, to name just a few. Because I set the "pace" for nearly all cells in the body, a deficiency can result in "sluggishness" of virtually any bodily function.
Diagnosis
There is a simple, easy, and accurate test to find out if the thyroid gland is making a normal amount of me. This test looks at the amount of TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) present in the blood. It is highly sensitive. If one suspects that they may have low thyroid function, the TSH blood test is the first test that should be done. If the TSH is high, then blood thyroxine levels are low. This is because TSH is a hormone produced by the pituitary. TSH "tells" the thyroid gland how much of me to produce. When blood levels of me drop too low, the pituitary will send MORE thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) to the thyroid gland, in an effort to cause the thyroid to increase its production of me. Even if one has symptoms that suggest hypothyroidism, the TSH test may well be normal. This means that the thyroid gland is making sufficient amounts of me. In our current, conventional medical thinking, this means that there is no deficiency of me (:D) and therefore no condition of hypothyroidism.